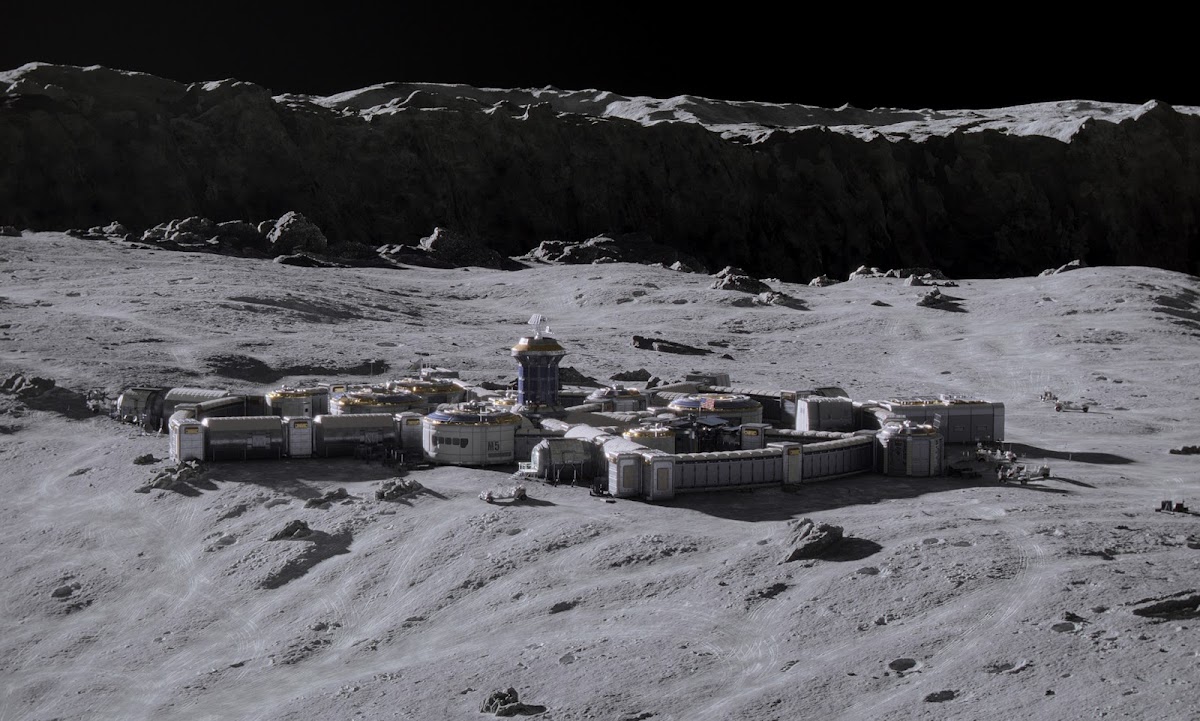
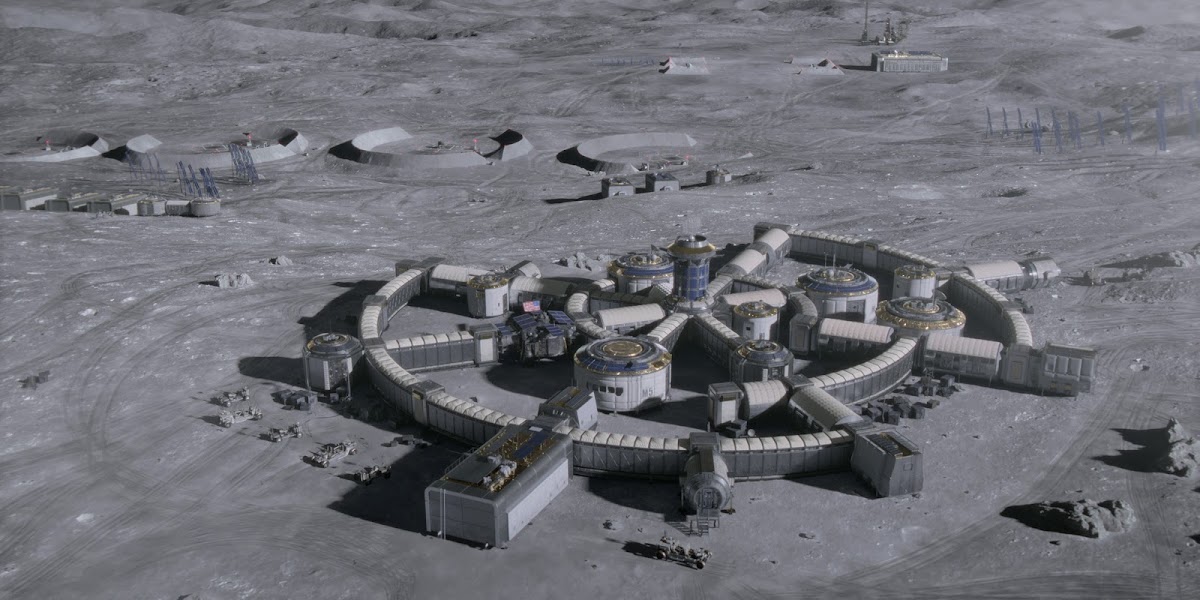
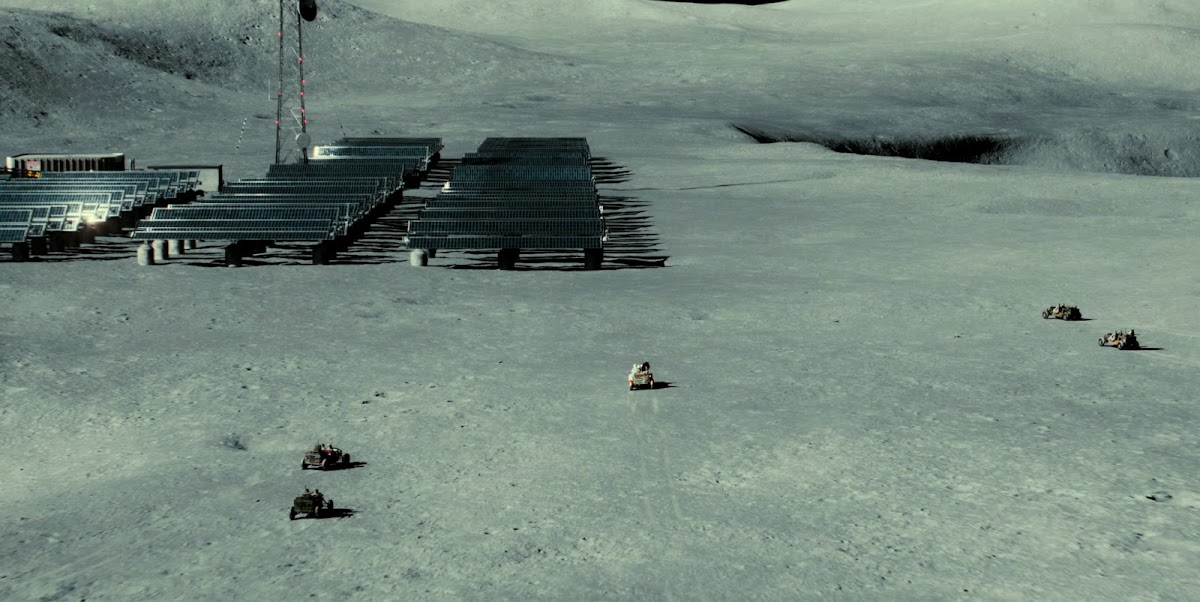
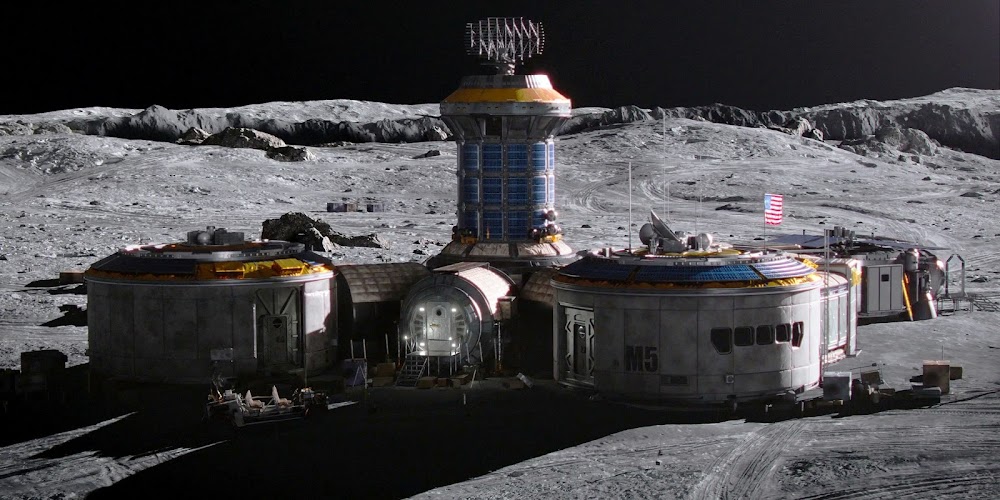
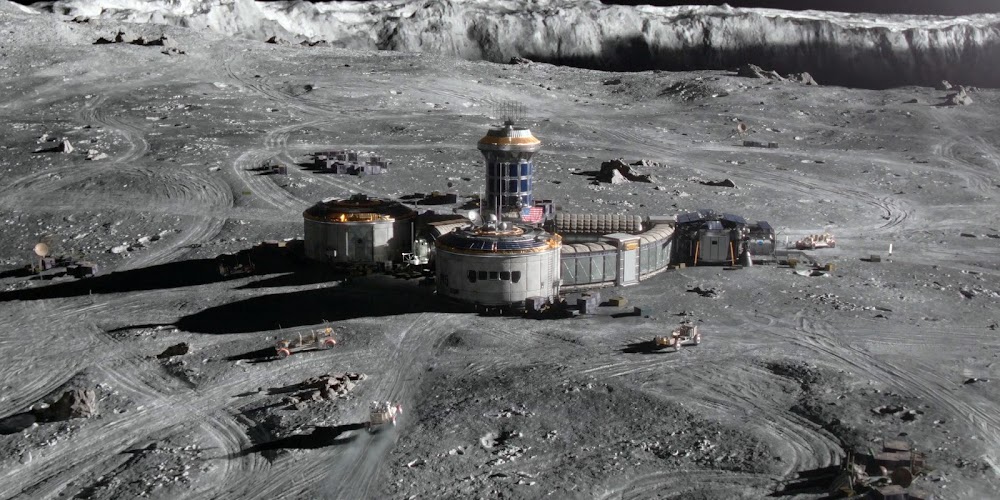
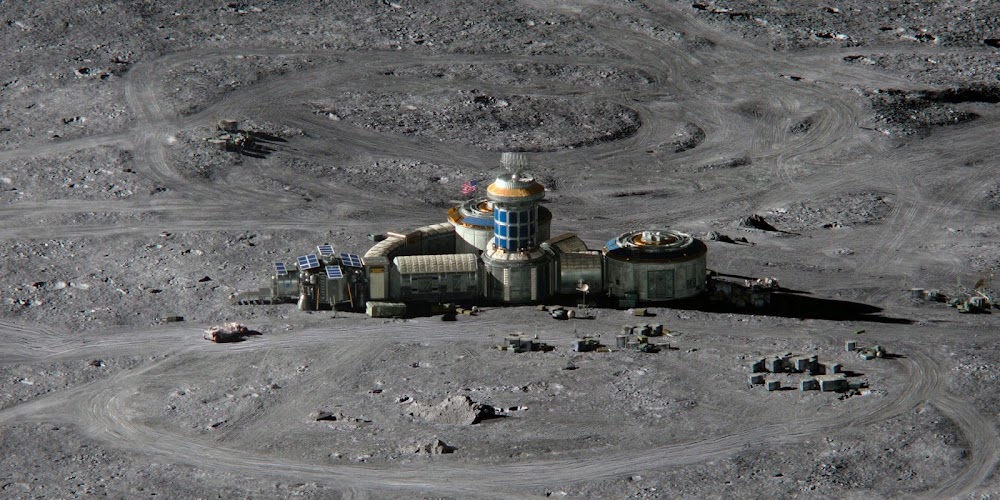
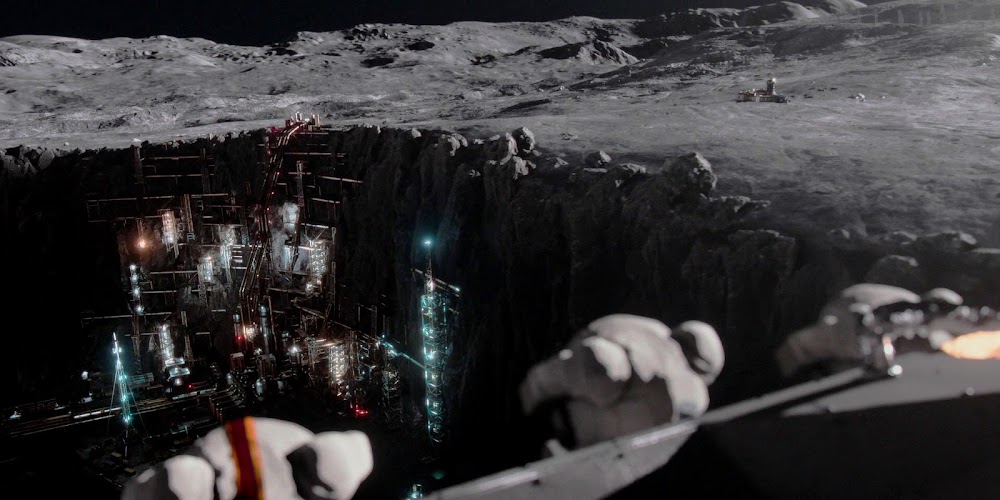
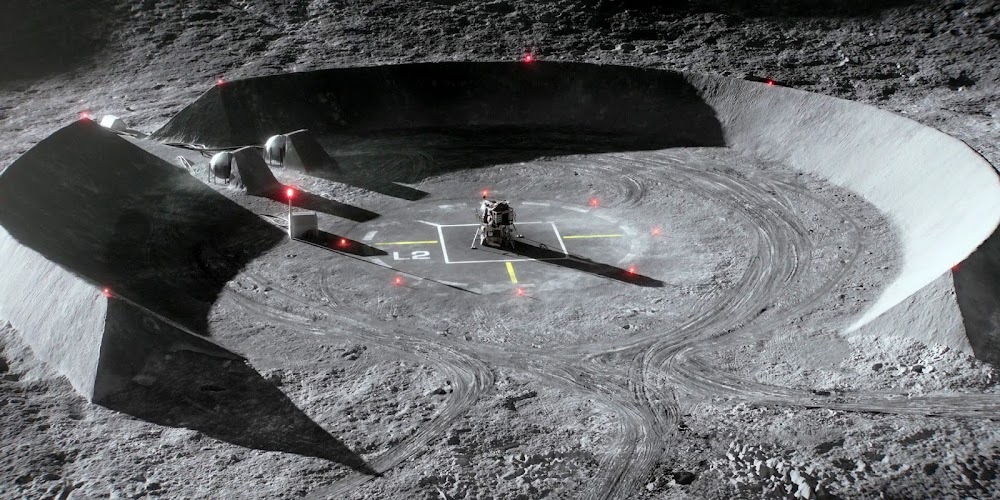
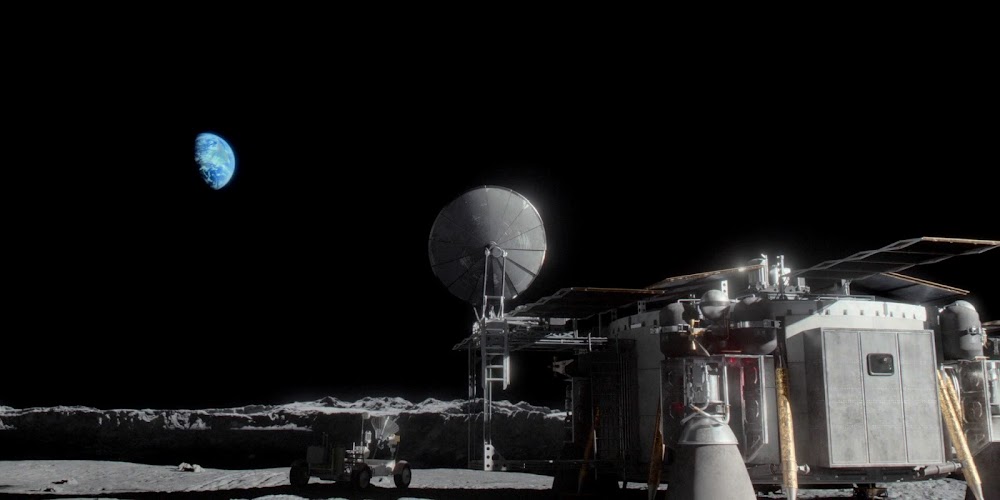
Concept renders for Artemis Base Camp by French scientific illustrator Pierre Carril, commissioned by the European Space Agency (ESA) in 2019. The concept depicts Artemis Base Camp having dome-shaped human habitats covered with a layer of lunar regolith for radiation and impact protection, interconnected transparent geodesic domes housing hydroponic gardens for food and oxygen generation, and vast deployable solar arrays capturing near-constant sunlight at the lunar south polar region to power the outpost. Astronauts in ESA-marked spacesuits oversee robotic construction rovers building the lunar base.
NASA's international Artemis Base Camp, with ESA as a major partner, is a planned long-term outpost on the lunar south pole, envisioned as the cornerstone of sustainable human exploration under the Artemis program, with establishment targeted for the 2030s. Situated near craters like Shackleton for access to water ice in permanently shadowed regions and areas of near-continuous sunlight for solar power, the initial base would include a fixed Foundation Surface Habitat to accommodate up to four astronauts for stays of one to two months, a pressurized rover for extended surface traverses, an unpressurized Lunar Terrain Vehicle for mobility, power systems (including potential nuclear options), in-situ resource utilization for producing essentials like oxygen and propellant from lunar regolith, and supporting infrastructure for scientific research and technology testing to pave the way for Mars missions. As of early 2026, with Artemis II crewed preparations advancing toward a March launch, the concept remains NASA's blueprint for transitioning from short landings to permanent lunar presence.
A competing project – International Lunar Research Station (ILRS) – is being developed under Chinese leadership and targets the lunar south pole region in the 2030s, starting robotic before permanent habitability post-2035 and full expansion by ~2050.
Showing posts with label Moon exploration. Show all posts
Showing posts with label Moon exploration. Show all posts
Sunday, February 8, 2026
Saturday, January 17, 2026
Lunar base in 'The Wandering Earth II' (2023) movie
The Wandering Earth II is a 2023 Chinese movie set in the mid-21st century as humanity races to save Earth from the Sun’s impending expansion into a red giant. The film chronicles the global effort to build thousands of massive planetary engines (and three more on the Moon) to propel the entire planet out of the Solar System - an audacious plan known as the Moving Mountain Project - while contending with the rival Digital Life Project that seeks to upload human consciousness into computers instead.
In the film, the Lunar bases for the three giant planetary engines built into Lunar crater rims are portrayed as sprawling, industrial megacomplexes carved into the Moon’s harsh terrain - towering gantries, clusters of spaceships on multiple launch pads, heavy lunar rovers kicking up plumes of regolith, and extensive networks of modular habitats, storage tanks, and processing plants illuminated by harsh artificial lights.
Here is a collection of Lunar scenery from the movie:
In the film, the Lunar bases for the three giant planetary engines built into Lunar crater rims are portrayed as sprawling, industrial megacomplexes carved into the Moon’s harsh terrain - towering gantries, clusters of spaceships on multiple launch pads, heavy lunar rovers kicking up plumes of regolith, and extensive networks of modular habitats, storage tanks, and processing plants illuminated by harsh artificial lights.
Here is a collection of Lunar scenery from the movie:
Saturday, November 1, 2025
Lunar Starship (HLS) interiors by SpaceX
On October 30, 2025, SpaceX provided a major update to its Lunar Starship (Human Landing System) program – a Lunar optimized Starship version which NASA has selected for the Artemis III and Artemis IV missions returning Americans to the surface of the Moon.
As it was written by SpaceX in the update: "Humanity is at an inflection point. For the first time in our existence, we possess the means, technology, and, for the moment, the will to establish a permanent human presence beyond Earth. Starship is designed to make this future a reality and is singularly capable of carrying unparalleled numbers of explorers and the building blocks they’ll need to establish the first outposts on lunar and other planetary surfaces. For these reasons and more, it was chosen to fulfill the key role of landing the first astronauts on the Moon in more than 50 years. It will be a central enabler that will fulfill the vision of NASA’s Artemis program, which seeks to establish a lasting presence on the lunar surface, not just flags and footprints, and ultimately forge the path to land the first humans on Mars. Starship provides unmatched capability to explore the Moon, thanks to its large size and ability to refill propellant in space. One single Starship has a pressurized habitable volume of more than 600 cubic meters, which is roughly two-thirds the pressurized volume of the entire International Space Station, and is complete with a cabin that can be scaled for large numbers of explorers and dual airlocks for surface exploration."
The update was accompanied with several new official renders of SpaceX's Lunar Starship, including its interior views.
As it was written by SpaceX in the update: "Humanity is at an inflection point. For the first time in our existence, we possess the means, technology, and, for the moment, the will to establish a permanent human presence beyond Earth. Starship is designed to make this future a reality and is singularly capable of carrying unparalleled numbers of explorers and the building blocks they’ll need to establish the first outposts on lunar and other planetary surfaces. For these reasons and more, it was chosen to fulfill the key role of landing the first astronauts on the Moon in more than 50 years. It will be a central enabler that will fulfill the vision of NASA’s Artemis program, which seeks to establish a lasting presence on the lunar surface, not just flags and footprints, and ultimately forge the path to land the first humans on Mars. Starship provides unmatched capability to explore the Moon, thanks to its large size and ability to refill propellant in space. One single Starship has a pressurized habitable volume of more than 600 cubic meters, which is roughly two-thirds the pressurized volume of the entire International Space Station, and is complete with a cabin that can be scaled for large numbers of explorers and dual airlocks for surface exploration."
The update was accompanied with several new official renders of SpaceX's Lunar Starship, including its interior views.
Airlock:
Cockpit:
Sunday, October 26, 2025
Infographic: Artemis landers (Starship HLS & Blue Moon MK2) vs Apollo Lunar Module
Recently NASA published an update on Human Landing System (HLS) program for Artemis missions. The presentation included, among other things, infographics about the SpaceX Lunar Starship (Human Landing System) for Artemis III and Artemis IV missions, the Blue Origin Blue Moon MK2 lander for the Artemis V mission, a comparison of both Lunar landers with the Apollo Lunar Module, as well as a Map of Artemis III candidate Landing sites.
SpaceX Lunar Starship (Human Landing System):
Blue Origin Blue Moon MK2 lander:
Map of Artemis III candidate Landing sites:
Wednesday, April 23, 2025
Can China beat the US in the 2nd Space race to the Moon?
The Moon, a celestial body last visited by humans during the Apollo 17 mission in 1972, is once again at the forefront of a new space race. Both the United States and China have outlined ambitious plans to return astronauts to the lunar surface and establish permanent bases, signaling a new era of lunar competition. In recent years China has shown rapid progress in robotic exploration of the Moon, including its far side, but can China actually surpass the US in returning humans to the Moon and establishing a continuous human presence there?
China's lunar ambitions are encapsulated in the Chinese Lunar Exploration Program, also known as the Chang'e program, named after the mythical moon goddess. This program has currently progressed through several phases, with the future phases focusing on manned missions and base construction:
China's Lunar Exploration Program: Plans and Timeline
China's lunar ambitions are encapsulated in the Chinese Lunar Exploration Program, also known as the Chang'e program, named after the mythical moon goddess. This program has currently progressed through several phases, with the future phases focusing on manned missions and base construction:
- Phase 1: Orbiting (2007-2010): Chang'e 1 and 2 successfully orbited the Moon, mapping its surface and testing technologies, laying the groundwork for subsequent missions.
- Phase 2: Robotic landing (2013-2019): Chang'e 3 (2013) and Chang'e 4 (2019) achieved soft landings, with Chang'e 4 notably landing on the far side of the Moon, a first in space exploration history.
- Phase 3: Sample return (2020-2024): Chang'e 5 (2020) and Chang'e 6 (2024) returned lunar samples, with Chang'e 6 being the first to collect from the far side, enhancing understanding of lunar composition.
- Phase 4: Robotic research station (2026-2028): The goal of Phase 4 is the development of an autonomous lunar research station near the Moon's south pole. Chang’e 7 (2026) will survey the south pole for water-ice and test in situ resource utilization (ISRU). Chang’e 8 (2028) will demonstrate advanced technologies including 3D-printed structures and ISRU methods critical for a future habitat.
- Phase 5: Manned landing (2029-2030): China's National Space Administration (CNSA) aims to land its first two-person crew on the lunar surface by 2030 (in some recent presentations even 2029), using a Lanyue lander and a Mengzhou re-entry capsule launched by heavy-lift Long March 10 rockets from Hainan’s Wenchang site. Large-scale tests of the lander and capsule systems are “on schedule,” though experts note China still trails NASA in overall crewed lunar infrastructure.
- Phase 6: International Lunar Research Station (ILRS) (2035): China aims to establish ILRS in the 2030s, initially as a robotic base, with plans to make it permanently habitable after 2035. The first phase of the lunar base is expected to be completed around 2035, with an extended model by 2050, located near the lunar south pole for access to water ice.
Saturday, November 23, 2024
New design for SpaceX Lunar Starship
During the livestream of Starship Flight test 6 SpaceX presented a new design for the Lunar Starship (Human Landing System) which NASA has selected for the Artemis missions returning humans to the surface of the Moon. According to the current schedule SpaceX is tasked to get Artemis III crew on the surface of the Moon in the end of 2026; we estimate this mission will slip for about two years – to 2028 because developing a human-rated spacecraft is a lot harder task than building "just" a cargo rocket.
An upgraded Lunar Starship for later Artemis missions:
Sunday, April 28, 2024
NASA has revealed new designs of lunar cargo landers from SpaceX & Blue Origin
As we know NASA has contracted SpaceX and Blue Origin to provide landing systems to take astronauts to the Moon’s surface from lunar orbit, beginning with SpaceX's Lunar Starship for Artemis III mission.
On April 19, 2024, NASA announced it has asked SpaceX and Blue Origin to develop cargo versions of their human lunar landers as an option under their existing contracts. These cargo variants are expected to land approximately 12 to 15 metric tons (26,000 to 33,000 pounds) of payload on the lunar surface and be in service no earlier than the Artemis VII mission. In the announcement NASA shared the latest official renders of lunar cargo landers from SpaceX and Blue Origin:
On April 19, 2024, NASA announced it has asked SpaceX and Blue Origin to develop cargo versions of their human lunar landers as an option under their existing contracts. These cargo variants are expected to land approximately 12 to 15 metric tons (26,000 to 33,000 pounds) of payload on the lunar surface and be in service no earlier than the Artemis VII mission. In the announcement NASA shared the latest official renders of lunar cargo landers from SpaceX and Blue Origin:
SpaceX's Lunar cargo Starship
Blue Origin's Lunar cargo Lander
Saturday, July 29, 2023
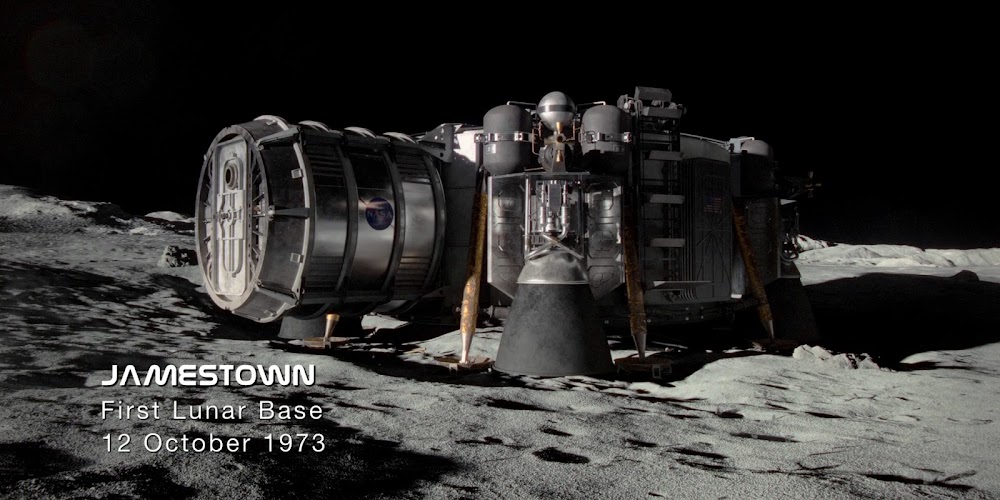
Jamestown US Moon base in "For All Mankind" season 3
Unlike the first two seasons, which focused on the Moon, season 3 of For All Mankind (an alternate history sci-fi TV series) focuses on Mars. But despite the Jamestown US Moon base being featured only briefly in the season, we can see it has been expanded significantly during the alternate history decade between season 2 (depicting 1983) and season 3 (depicting 1992 to 1995), completing the 1st ring of modules and adding a 2nd ring. So, in this alternate reality of the show development on the Moon has not been neglected because of the Mars mission.
NASA's Sojourner at Jamestown preparing for the mission to Mars:
Wednesday, December 7, 2022
Lunar colony in Ad Astra (2019) movie
Ad Astra is 2019 science fiction thriller set in mid-21st century when humanity has started to settle the inner Solar System. One of the most memorable parts of the movie is human colony on the Moon with space pirates :) chasing military rover convoy going to the spaceport on the far side of the Moon.
In the movie a son (Brad Pitt), serving in the military, is sent on a mission to uncover the truth about his famous father's (Tommy Lee Jones) long lost mission near Neptune which now threatens the survival of Earth. In his lonesome and dangerous mission he visits several places including a dynamic but wild human colony on the Moon and a desolate relay station on Mars. Here is a collection of HD images from the Lunar part of the movie:
In the movie a son (Brad Pitt), serving in the military, is sent on a mission to uncover the truth about his famous father's (Tommy Lee Jones) long lost mission near Neptune which now threatens the survival of Earth. In his lonesome and dangerous mission he visits several places including a dynamic but wild human colony on the Moon and a desolate relay station on Mars. Here is a collection of HD images from the Lunar part of the movie:
Sunday, September 4, 2022
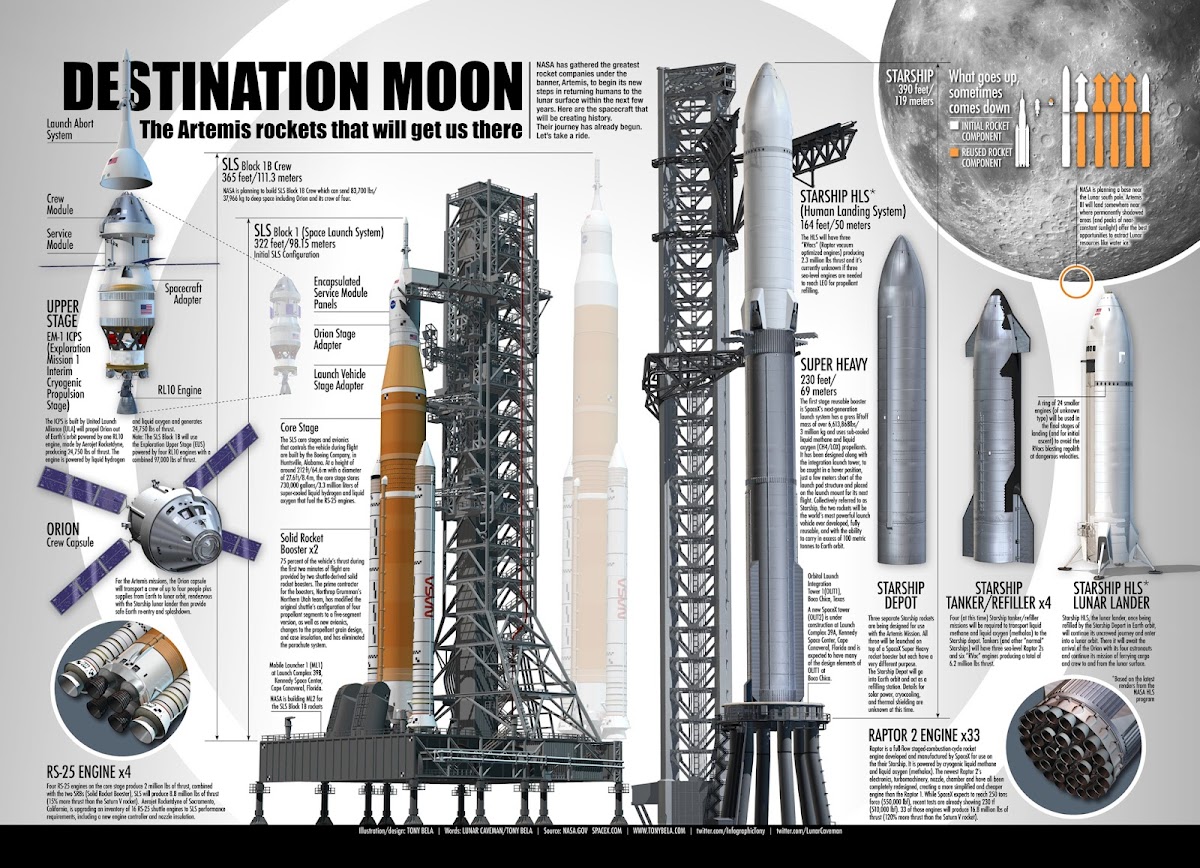
Artemis rockets (SLS & Starship) that will get us to the Moon - infographic by Tony Bela
Australian space illustrator Tony Bela has created an infographic of Artemis rockets – NASA's Space Launch System (SLS), boosting Orion crew capsule to lunar orbit, and SpaceX's Human Landing System (known as Lunar Starship) – that will get the humanity back to the surface of the Moon.
You can download the infographic in its original resolution here.
Tuesday, August 3, 2021
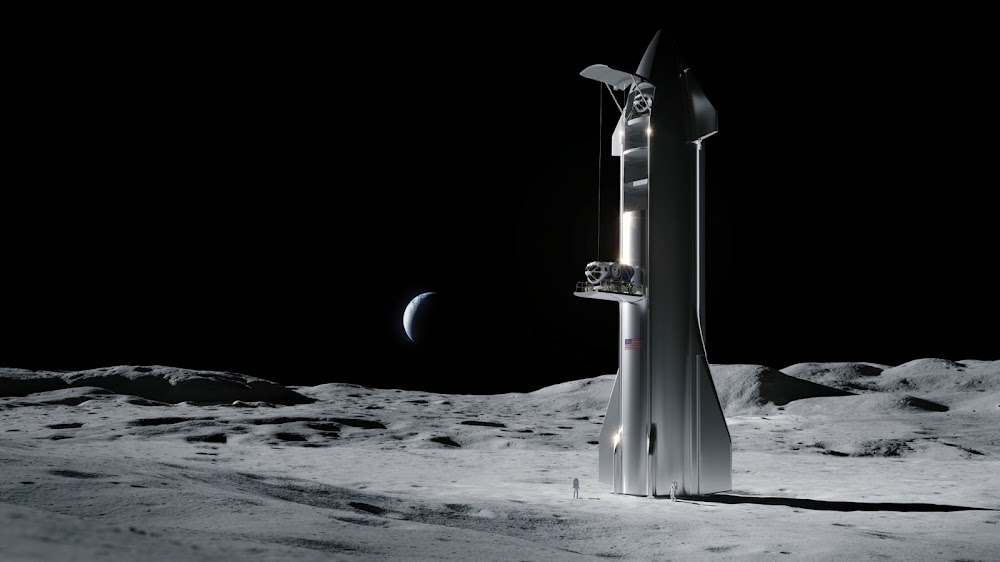
SpaceX Lunar Starship delivering cargo for Artemis Base Camp
SpaceX's Lunar Starship, selected to return humans to the Moon, delivering cargo and crew for NASA's Artemis Base Camp on the Moon's South Pole. Concept artwork created by US 3D artist Nick Henning.
Sunday, May 16, 2021
Lunar scenes in season 2 of "For All Mankind" alternate history TV series
Season 2 really kicked up the space race on Lunar surface in For All Mankind alternate history sci-fi TV series exploring the idea of never ending space race if Soviets would have beaten US in the race for the Moon. In season 1, depicting the events in alternate 1969 to 1974, both Soviets and US start building their separate bases at the rim of Shackleton Crater near the lunar South pole. In season 2, depicting the alternate 1983, both bases have been expanded and the superpowers compete for resources on the Lunar surface. The Cold War is very close to becoming a hot one.
The intention of the show is to jump about a decade further into the increasingly diverging reality of the show each season. The final scene of season 2 hints Mars will be the central stage in season 3. We are eagerly waiting to see how the authors of the show will have imagined humanity's journey to Mars in their alternate reality. The filming of season 3 has already started.
The intention of the show is to jump about a decade further into the increasingly diverging reality of the show each season. The final scene of season 2 hints Mars will be the central stage in season 3. We are eagerly waiting to see how the authors of the show will have imagined humanity's journey to Mars in their alternate reality. The filming of season 3 has already started.
Jamestown US Moon base in 1983:
US mining site at Jamestown base:
Overview of the Jamestown base:
One of Jamestown's landing pads:
Friday, April 16, 2021
NASA selects SpaceX Lunar Starship to return humans to the Moon
 Today NASA announced it has selected SpaceX "to continue development of the first commercial human lander that will safely carry the next two American astronauts to the lunar surface" as part of the Artemis program. A year ago it was announced three contenders were selected to compete for this mission - SpaceX, Blue Origin's led "National Team" and Dynetics - and SpaceX revealed it is working for a lunar optimized Starship. Now we know SpaceX's proposal has won the race. In a milestone-based fixed-price contract SpaceX will be able to receive $2.89 billion to develop the Lunar Starship. The year when SpaceX needs to land humans back to the Moon is not specified yet.
Today NASA announced it has selected SpaceX "to continue development of the first commercial human lander that will safely carry the next two American astronauts to the lunar surface" as part of the Artemis program. A year ago it was announced three contenders were selected to compete for this mission - SpaceX, Blue Origin's led "National Team" and Dynetics - and SpaceX revealed it is working for a lunar optimized Starship. Now we know SpaceX's proposal has won the race. In a milestone-based fixed-price contract SpaceX will be able to receive $2.89 billion to develop the Lunar Starship. The year when SpaceX needs to land humans back to the Moon is not specified yet.In addition to today's announcement, NASA shared latest official render of SpaceX's Lunar Starship which slightly differs from last year's version:
Monday, March 29, 2021
Jamestown US Moon base in season 1 of "For All Mankind" TV series
For All Mankind is alternate history sci-fi TV series depicting what could have happened if the space race had never ended after the Soviet Union succeeds in the first crewed Moon landing ahead of the United States in 1969. The authors of the show speculate such an event would force US to double down on space exploration altering the Apollo program from "flags and footprints" approach to a more ambitious one with extensive infrastructure buildup on the Moon (with hints of Mars exploration in later seasons of the show). Pouring money and resources into space exploration creates an atmosphere every space nerd would have wanted to continue after the enthusiastic 1960s.
Season 1 of the series (aired in 2019) depicts events from 1969 to 1974 in the alternate timeline of For All Mankind. The series are in the middle of season 2 now depicting the alternate 1983. It was said each season of the show will jump about a decade further into the increasingly diverging reality of the show. We will feature season 2 here after it will be aired completely. So here is a collection of HD images from season 1 with a focus on US Jamestown lunar base at the rim of Shackleton Crater near the lunar South pole where water ice is discovered in 1970 (several decades earlier than in reality):
Season 1 of the series (aired in 2019) depicts events from 1969 to 1974 in the alternate timeline of For All Mankind. The series are in the middle of season 2 now depicting the alternate 1983. It was said each season of the show will jump about a decade further into the increasingly diverging reality of the show. We will feature season 2 here after it will be aired completely. So here is a collection of HD images from season 1 with a focus on US Jamestown lunar base at the rim of Shackleton Crater near the lunar South pole where water ice is discovered in 1970 (several decades earlier than in reality):
Landing of the initial Jamestown lunar base module in October 1973:
Jamestown Phase 1 US lunar base in 1974:
Wednesday, March 3, 2021
Updated design of #dearMoon Starship (2021)
On March 3 dearMoon Project opened application process for 8 crew member spots on SpaceX's first crewed deep space mission - #dearMoon Starship flight around the Moon scheduled for 2023. Applications are open for everyone now, not just the artists as originally was planned. The applications page contains some official renders of Starship's updated design with the most visible differences being in main window design:
Sunday, September 6, 2020
Short film: honeymoon trip to the Moon with SpaceX Starship
Two brothers from DeepSpaceCourier have created an animated short film of a newly married couple taking their honeymoon trip to the Moon with SpaceX's Starship. The short film starts with the couple boarding Starship Super Heavy at ocean launch platform; Starship is launched to the Moon and after a few days voyage docks to Lunar Gateway; there the couple switches to a Lunar Starship and lands on the surface of the Moon.

Some images from the short film in chronological order:

Thursday, April 30, 2020
NASA selects SpaceX's lunar optimized Starship for Artemis program
Today NASA announced that three US companies - SpaceX, Blue Origin & Dynetics - will develop the human landers that will land astronauts on the Moon beginning in 2024 as part of the Artemis program. And SpaceX shared some renders of the "lunar optimized Starship" which is developed "to transport crew between lunar orbit and the surface of the Moon". SpaceX added that "a lunar optimized Starship can fly many times between the surface of the Moon and lunar orbit without flaps or heat shielding required for Earth return. With large habitable and storage volume, Starship is capable of delivering significant amounts of cargo for research and to support robust operations on the lunar surface to enable a sustainable Moon base."
Sunday, January 26, 2020
SpaceX Starship landing on the Moon - video animation by Hazegrayart
Video animation of SpaceX's Starship traveling to and landing on the Moon by HazeGrayArt who is known for his superb animations of both real and paper rockets, spacecraft and aircraft on his YouTube channel. He has also made animations of the previous iterations of Starship - Tintin-style BFR v2018 and delta-winged BFR v2017 - landing on Mars; and BFR v2017 landing on the Moon.
Tuesday, November 19, 2019
HD quality official render of SpaceX cargo Starship unloading on the Moon
3 weeks ago SpaceX's Principal Mars Development Engineer Paul Wooster gave a presentation "SpaceX's Plans for Sending Humans to Mars" at 22nd Annual Mars Society Convention. In the presentation there was a new render of the redesigned SpaceX's cargo Starship unloading some NASA rovers on Lunar surface. Unfortunately no one was able to capture a decent quality image of the render then. Yesterday the render was posted on NASA's web page in high quality:
The post reveals that SpaceX is one of companies taking part in NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) initiative which "allows rapid acquisition of lunar delivery services for payloads that advance capabilities for science, exploration, or commercial development of the Moon. Investigations and demonstrations launched on commercial Moon flights will help the agency study Earth’s nearest neighbor under the Artemis program. As its next step in exploration, NASA is preparing to send the first woman and next man to the Moon by 2024, establish sustainable lunar exploration by 2028, and plans to send astronauts to Mars in the mid-2030s."
The post reveals that SpaceX is one of companies taking part in NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) initiative which "allows rapid acquisition of lunar delivery services for payloads that advance capabilities for science, exploration, or commercial development of the Moon. Investigations and demonstrations launched on commercial Moon flights will help the agency study Earth’s nearest neighbor under the Artemis program. As its next step in exploration, NASA is preparing to send the first woman and next man to the Moon by 2024, establish sustainable lunar exploration by 2028, and plans to send astronauts to Mars in the mid-2030s."
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)